- LOGIN
- MemberShip
- 2025-12-17 17:45:37
- 'Mounjaro' confirmed to have reimb appropriateness
- by Son, Hyung Min | translator | 2025-12-17 09:51:08
There are ongoing concerns that the treatment landscape for Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) in South Korea is facing limitations.
While this issue persists, the GLP-1/GIP receptor dual agonist Mounjaro has passed the initial hurdle for national health insurance reimbursement coverage for diabetes, drawing significant attention to whether it will lead to a paradigm shift in domestic treatment.
According to industry sources on December 17, Mounjaro (tirzepatide) passed the initial stage for national health insurance reimbursement earlier this month. Consequently, Mounjaro's developer, Eli Lilly, will now enter price negotiations with the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS). Lilly has been pursuing reimbursement for Mounjaro since early 2024, achieving the positive result after approximately two years.
Lilly confirmed that Mounjaro demonstrated improved clinical utility compared to comparator drugs. Following discussions on cost-effectiveness based on economic evaluation with the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA), Mounjaro was considered for the final Drug Reimbursement Evaluation Committee (DREC) meeting of the year and was received reimbursement appropriateness decision.
Experts anticipate that the remaining steps will proceed quickly, given Mounjaro’s acknowledged clinical value, economic feasibility, and necessity within the domestic treatment environment.

T2D diabetes management becomes harder over time...demands for new treatment option↑
Given rising obesity rates and an aging population, there is a growing demand for treatment options that can manage not only blood glucose but also body weight and overall metabolism. T2D is a chronic condition where prolonged disease duration leads to cumulative decline in insulin secretion function and increased insulin resistance, resulting in a significant number of patients failing to reach target blood glucose levels with conventional strategies alone.
According to the 2025 Factsheet by the Korean Diabetes Association, 6 out of 10 diabetes patients in South Korea are not achieving the treatment goal of a hemoglobin A1c (H1A1c) level of 6.5%. T2D is a progressive disease with difficulty achieving remission. With prolonged disease duration, pancreatic insulin secretion deteriorates, worsening insulin resistance and leading to difficulties in glucose regulation.
The prevalence of obesity is also rising. Over half of diabetes patients (52.4%) are also obese, and 61.1% have abdominal obesity. Conversely, the prevalence of diabetes among the obese population is 17.6%, about twice as high as in the non-obese population. Among the obese population aged 65 and over, one in three (31.6%) has co-morbid diabetes.
The problem is that, in patients with high Body Mass Index (BMI), visceral fat contributes to insulin resistance, and inflammatory responses in adipose tissue impair insulin action. This not only makes blood glucose management difficult but also reduces overall metabolic function. Consequently, blood glucose regulation can be challenging with conventional oral treatments or insulin alone.
Failure to control blood glucose in T2D patients increases the risk of various complications, including retinopathy, neuropathy, stroke, angina, and myocardial infarction due to arteriosclerosis. One study showed that T2D patients who fail to control their blood glucose have a 2–3 times higher risk of cardiovascular disease in men and 3–5 times higher risk in women compared to the general population.
Thus, there is high demand among healthcare providers and patients for GLP-1 class treatments that offer benefits not only in blood glucose control and weight loss but also in overall metabolic health. Mounjaro, which can be administered once weekly, is the first and only therapeutic agent designed to bind to and activate both GLP-1 and GIP receptors selectively.
Mounjaro has mechanistic advantages that stimulate insulin secretion, improve insulin sensitivity, lower glucagon levels to lower blood glucose, and delay gastric emptying to reduce food intake, leading to weight loss.
Mounjaro demonstrated superior HbA1c reduction across all doses compared to all comparator arms in the five Phase 3 clinical trials (SURPASS 1–5) involving T2D patients.
The achievement rate of the T2D treatment goal, which is HbA1c level below 6.5%, in the Mounjaro group was up to 95% (SURPASS-5, 10mg), and the achievement rate of HbA1c < 5.7%, indicating a near-normal blood glucose level, reached up to 62% (SURPASS-5, 15mg). Furthermore, since a weight reduction of over 10% significantly improves blood glucose in T2D patients, up to 69% of patients in the Mounjaro group achieved this goal (SURPASS-3, 15mg).
Notably, despite effective blood glucose reduction, the risk of clinically significant or severe hypoglycemia did not increase compared to the control groups.
This means that even patients whose treatment options were limited by hypoglycemia risk can now expect to reach their target blood glucose (HbA1c < 6.5%) and achieve higher levels of glycemic control with Mounjaro.
Mounjaro recommended in major guidelines..."Effective strategy needed for long-term metabolic health"
In October, the Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) issued a statement emphasizing the need to manage comorbid conditions in T2D. A key change in the KDA's newly proposed T2D management algorithm is the initial separate listing of the GIP/GLP-1 receptor dual agonist from existing GLP-1 receptor agonists. The KDA also specified the GIP/GLP-1 receptor dual agonist as a preferred medication for T2D patients with co-morbid obesity.
Professor Byung-Wan Lee (Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University, Severance Hospital), who directed Guidelines for the KDA stressed, "T2D patients with co-morbid obesity require a more effective treatment strategy that includes weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity, in addition to overall and long-term metabolic health improvement."
Professor Lee stated, "It is significant that, following the last guideline revision where Mounjaro was first listed as a distinct component name separate from existing GLP-1 receptor agonists to emphasize its efficacy in blood glucose and weight control, this algorithm update reconfirms the clinical utility of the GIP/GLP-1 receptor dual agonist in T2D patients with obesity."
He added, "For T2D patients with obesity who failed to reach target blood glucose levels even with existing oral treatments or insulin, We hope access to Mounjaro is improved as quickly as possible so that these patients can benefit from Mounjaro's blood glucose and weight loss results."
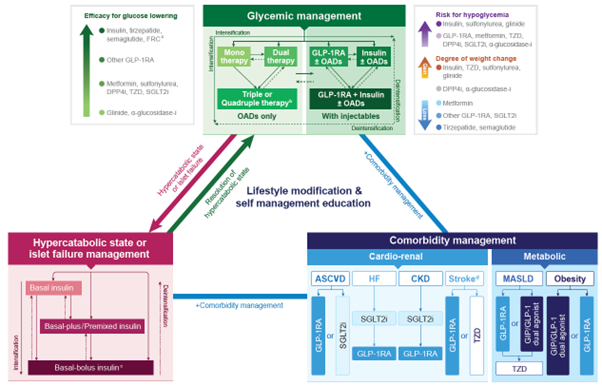
Based on Mounjaro's clinical and practical value, domestic and international guidelines categorize it separately from existing GLP-1 receptor agonists. Furthermore, the World Health Organization (WHO) designated Mounjaro as an Essential Medicine in September for T2D patients with comorbid conditions such as obesity.
This decision is significant as it officially recognizes Mounjaro as an essential, public-health-critical drug for T2D treatment with co-morbid obesity, underscoring the need to improve access through expanded insurance coverage.
Professor Lee stated, "In a situation where the number of T2D patients with obesity is rising, ensuring accessibility to innovative treatments that can improve overall metabolic health beyond simple blood glucose reduction, regardless of economic status, is beneficial, both for individual patients and for long-term national health improvement," and added, "As Mounjaro has been recognized globally as an essential medicine for T2D patients with obesity, prompt policy action is needed so that it can be managed under the system and safely used by patients who critically need it."
-

- 0
댓글 운영방식은
댓글은 실명게재와 익명게재 방식이 있으며, 실명은 이름과 아이디가 노출됩니다. 익명은 필명으로 등록 가능하며, 대댓글은 익명으로 등록 가능합니다.
댓글 노출방식은
댓글 명예자문위원(팜-코니언-필기모양 아이콘)으로 위촉된 데일리팜 회원의 댓글은 ‘게시판형 보기’와 ’펼쳐보기형’ 리스트에서 항상 최상단에 노출됩니다. 새로운 댓글을 올리는 일반회원은 ‘게시판형’과 ‘펼쳐보기형’ 모두 팜코니언 회원이 쓴 댓글의 하단에 실시간 노출됩니다.
댓글의 삭제 기준은
다음의 경우 사전 통보없이 삭제하고 아이디 이용정지 또는 영구 가입제한이 될 수도 있습니다.
-
저작권·인격권 등 타인의 권리를 침해하는 경우
상용 프로그램의 등록과 게재, 배포를 안내하는 게시물
타인 또는 제3자의 저작권 및 기타 권리를 침해한 내용을 담은 게시물
-
근거 없는 비방·명예를 훼손하는 게시물
특정 이용자 및 개인에 대한 인신 공격적인 내용의 글 및 직접적인 욕설이 사용된 경우
특정 지역 및 종교간의 감정대립을 조장하는 내용
사실 확인이 안된 소문을 유포 시키는 경우
욕설과 비어, 속어를 담은 내용
정당법 및 공직선거법, 관계 법령에 저촉되는 경우(선관위 요청 시 즉시 삭제)
특정 지역이나 단체를 비하하는 경우
특정인의 명예를 훼손하여 해당인이 삭제를 요청하는 경우
특정인의 개인정보(주민등록번호, 전화, 상세주소 등)를 무단으로 게시하는 경우
타인의 ID 혹은 닉네임을 도용하는 경우
-
게시판 특성상 제한되는 내용
서비스 주제와 맞지 않는 내용의 글을 게재한 경우
동일 내용의 연속 게재 및 여러 기사에 중복 게재한 경우
부분적으로 변경하여 반복 게재하는 경우도 포함
제목과 관련 없는 내용의 게시물, 제목과 본문이 무관한 경우
돈벌기 및 직·간접 상업적 목적의 내용이 포함된 게시물
게시물 읽기 유도 등을 위해 내용과 무관한 제목을 사용한 경우
-
수사기관 등의 공식적인 요청이 있는 경우
-
기타사항
각 서비스의 필요성에 따라 미리 공지한 경우
기타 법률에 저촉되는 정보 게재를 목적으로 할 경우
기타 원만한 운영을 위해 운영자가 필요하다고 판단되는 내용
-
사실 관계 확인 후 삭제
저작권자로부터 허락받지 않은 내용을 무단 게재, 복제, 배포하는 경우
타인의 초상권을 침해하거나 개인정보를 유출하는 경우
당사에 제공한 이용자의 정보가 허위인 경우 (타인의 ID, 비밀번호 도용 등)
※이상의 내용중 일부 사항에 적용될 경우 이용약관 및 관련 법률에 의해 제재를 받으실 수도 있으며, 민·형사상 처벌을 받을 수도 있습니다.
※위에 명시되지 않은 내용이더라도 불법적인 내용으로 판단되거나 데일리팜 서비스에 바람직하지 않다고 판단되는 경우는 선 조치 이후 본 관리 기준을 수정 공시하겠습니다.
※기타 문의 사항은 데일리팜 운영자에게 연락주십시오. 메일 주소는 dailypharm@dailypharm.com입니다.










