- LOGIN
- MemberShip
- 2026-01-02 06:33:33
- US and Japan ease new drug approval reviews
- by Cha, Ji-Hyun | translator | 2025-12-31 07:49:55
As the global biopharmaceutical market grows rapidly, competition among major countries' regulatory authorities over expedited drug reviews has intensified. As the success or failure of new drug development hinges critically on launch timing, nations are engaging in a ‘speed race’ by shortening review timelines and expanding conditional approvals. While Korea has also moved to streamline approval procedures, experts say additional measures are needed to improve the effectiveness and real-world impact of the system.
According to the 2025 Biopharmaceutical Industry Trends Report published by the Korea Biomedicine Industry Association(KoBIA) on the 30th, the global biopharmaceutical market has been growing at a double-digit annual rate and has become the central pillar of the pharmaceutical industry. In 2024, the global biopharmaceutical market reached USD 632.3 billion, representing an annual growth rate of 13.6%, and is projected to grow to USD 974.2 billion by 2028.
As the market expands, competition among regulatory authorities worldwide to accelerate their approval timeline has also intensified. Countries are strategically leveraging fast-track review and conditional approval pathways to expedite new drug launches and gain an edge in the global approval race.
The United States and Japan are currently at the forefront of expedited review frameworks.
First, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is establishing a multi-layered expedited review system, including ▲Fast Track, ▲Breakthrough Therapy, ▲Accelerated Approval, and ▲Priority Review.
The Fast Track designation applies to drugs intended to treat serious or life-threatening conditions that address unmet medical needs. Under this program, the FDA provides more frequent communication and guidance from the development stage and allows rolling submission and review of data, minimizing bottlenecks throughout development and review.
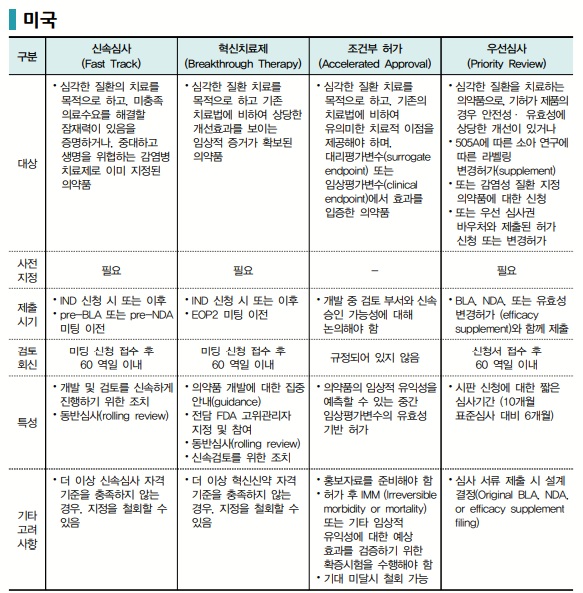
The Breakthrough Therapy designation is a more advanced program than Fast Track and is granted when a drug demonstrates or is expected to demonstrate a significant clinical improvement over existing treatments in early clinical trials. When this program is applied, the FDA assigns a multidisciplinary review team to provide intensive support across clinical, statistical, and manufacturing aspects, helping applicants to finalize development strategies at an early stage.
Accelerated Approval allows early authorization based on surrogate endpoints or interim clinical indicators, without waiting for final clinical results. However, post-marketing confirmatory trials are mandatory upon approval, and the FDA may modify or revoke approval if clinical benefit is not demonstrated in these trials. This clear delineation of post-approval responsibility alongside expedited review is central to the U.S. accelerated approval system.
Priority Review that shortens the review period itself after an application is submitted. It directly accelerates the launch timeline of new drugs compared to standard review. It applies to treatments for serious diseases or those expected to yield significant public health benefits.
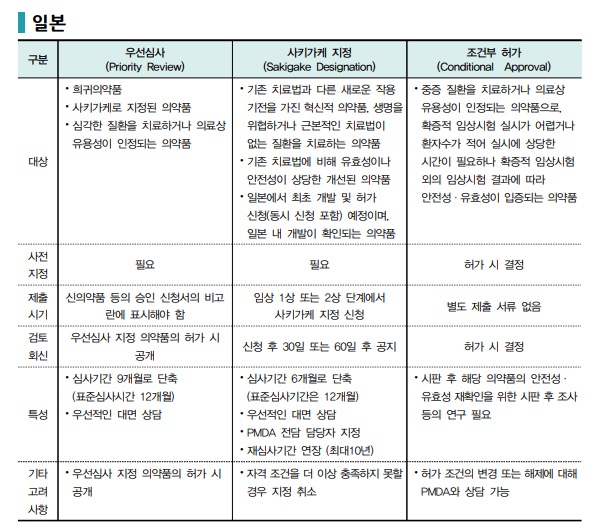
Japan adopts a strategy that directly guarantees corporate profitability. The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) supports early approval of innovative drugs primarily through Priority Review and the Sakigake program, while also fostering a regulatory environment that considers the potential for market success post-approval.
The Sakigake program is Japan's flagship fast-track review initiative for innovative new drugs for severe diseases that are expected to demonstrate superior clinical benefit over existing treatments. If a drug designated under Sakigake is the first in the world to apply for approval in Japan, the re-examination period can be extended up to 10 years. This effectively guarantees a long-term monopoly status equivalent to a patent, serving as a powerful incentive for global pharmaceutical companies to prioritize Japan as an initial launch market.
Rather than focusing solely on speed, Europe emphasizes regulatory differentiation based on the level of uncertainty. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) concurrently operates systems like Conditional Marketing Authorisation, Marketing Authorisation under Exceptional Circumstances, Accelerated Assessment, and the PRIority Medicines (PRIME) program, applying different approval pathways based on a drug's development stage and level of clinical evidence. The Marketing Authorisation under Exceptional Circumstances system acknowledges situations such as rare diseases where confirmatory trials may be impractical even after market entry, distinguishing Europe’s approach from other regions.
China is pursuing aggressive regulatory innovation centered on speed, accelerating its rise as a global biopharma powerhouse. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) operates multiple fast-track review systems, including Breakthrough Therapy Designation, Conditional Approval, Priority Review, and Special Approval.
Among these, the Special Approval system for public health emergencies is designed to initiate acceptance and initial review procedures within 24 hours, making it one of the fastest response systems globally. Priority review timelines have also been shortened significantly, from the standard 200 days to 130 days, reflecting China’s aggressive time-reduction strategy.
Korea has introduced expedited review and conditional approval systems in line with global regulatory trends. Through the GIFT (Global Innovative product on Fast Track) program, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) shortens review timelines for innovative drugs and treatments for serious or rare diseases, while allowing conditional approval before full clinical evidence is accumulated.
Under GIFT, the review period is reduced by approximately 25%, from 120 days to 90 days. Additionally, the system has institutionalized rolling review, where approval data is submitted and reviewed in stages, to enhance review efficiency.
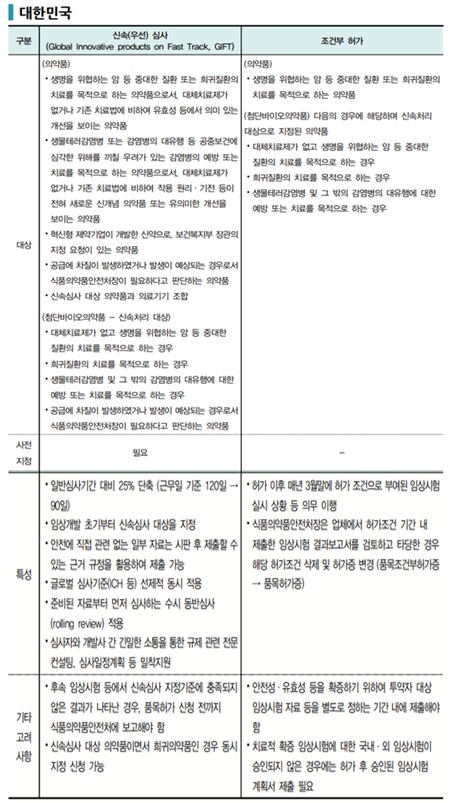
However, critics argue that Korea’s system still lags behind major countries in practical implementation. To achieve genuine global competitiveness, Korea’s GIFT program may require bold enhancements on par with those in leading jurisdictions. Just as Japan’s Sakigake program offers strong exclusivity incentives for first-in-world applications, Korea also needs to strengthen commercial incentives for companies by guaranteeing exclusivity for a certain period after approval or implementing exceptional drug pricing preferential policies.
Expanding the scientific flexibility of regulations and strengthening the expertise and authority of regulatory agencies are also identified as key tasks to enhance the competitiveness of the GIFT system. In areas with urgent unmet medical needs, such as cancer and rare diseases, there is an argument for more active acceptance of surrogate endpoints while shifting the regulatory paradigm toward strengthened post-marketing surveillance and post-approval verification. Analysis also suggests that strengthening the MFDS's bio-specialist workforce and institutionally guaranteeing the discretion and responsibility of reviewers must precede such changes.
An industry official commented, “We are now in an era where the quality of regulation directly determines a country’s biopharmaceutical competitiveness. Beyond simply accelerating approval timelines, the GIFT system's effectiveness will only truly increase when a clear commercial reward structure is established that allows for the recovery of the massive R&D costs invested in new drug development.”
-

- 0
댓글 운영방식은
댓글은 실명게재와 익명게재 방식이 있으며, 실명은 이름과 아이디가 노출됩니다. 익명은 필명으로 등록 가능하며, 대댓글은 익명으로 등록 가능합니다.
댓글 노출방식은
댓글 명예자문위원(팜-코니언-필기모양 아이콘)으로 위촉된 데일리팜 회원의 댓글은 ‘게시판형 보기’와 ’펼쳐보기형’ 리스트에서 항상 최상단에 노출됩니다. 새로운 댓글을 올리는 일반회원은 ‘게시판형’과 ‘펼쳐보기형’ 모두 팜코니언 회원이 쓴 댓글의 하단에 실시간 노출됩니다.
댓글의 삭제 기준은
다음의 경우 사전 통보없이 삭제하고 아이디 이용정지 또는 영구 가입제한이 될 수도 있습니다.
-
저작권·인격권 등 타인의 권리를 침해하는 경우
상용 프로그램의 등록과 게재, 배포를 안내하는 게시물
타인 또는 제3자의 저작권 및 기타 권리를 침해한 내용을 담은 게시물
-
근거 없는 비방·명예를 훼손하는 게시물
특정 이용자 및 개인에 대한 인신 공격적인 내용의 글 및 직접적인 욕설이 사용된 경우
특정 지역 및 종교간의 감정대립을 조장하는 내용
사실 확인이 안된 소문을 유포 시키는 경우
욕설과 비어, 속어를 담은 내용
정당법 및 공직선거법, 관계 법령에 저촉되는 경우(선관위 요청 시 즉시 삭제)
특정 지역이나 단체를 비하하는 경우
특정인의 명예를 훼손하여 해당인이 삭제를 요청하는 경우
특정인의 개인정보(주민등록번호, 전화, 상세주소 등)를 무단으로 게시하는 경우
타인의 ID 혹은 닉네임을 도용하는 경우
-
게시판 특성상 제한되는 내용
서비스 주제와 맞지 않는 내용의 글을 게재한 경우
동일 내용의 연속 게재 및 여러 기사에 중복 게재한 경우
부분적으로 변경하여 반복 게재하는 경우도 포함
제목과 관련 없는 내용의 게시물, 제목과 본문이 무관한 경우
돈벌기 및 직·간접 상업적 목적의 내용이 포함된 게시물
게시물 읽기 유도 등을 위해 내용과 무관한 제목을 사용한 경우
-
수사기관 등의 공식적인 요청이 있는 경우
-
기타사항
각 서비스의 필요성에 따라 미리 공지한 경우
기타 법률에 저촉되는 정보 게재를 목적으로 할 경우
기타 원만한 운영을 위해 운영자가 필요하다고 판단되는 내용
-
사실 관계 확인 후 삭제
저작권자로부터 허락받지 않은 내용을 무단 게재, 복제, 배포하는 경우
타인의 초상권을 침해하거나 개인정보를 유출하는 경우
당사에 제공한 이용자의 정보가 허위인 경우 (타인의 ID, 비밀번호 도용 등)
※이상의 내용중 일부 사항에 적용될 경우 이용약관 및 관련 법률에 의해 제재를 받으실 수도 있으며, 민·형사상 처벌을 받을 수도 있습니다.
※위에 명시되지 않은 내용이더라도 불법적인 내용으로 판단되거나 데일리팜 서비스에 바람직하지 않다고 판단되는 경우는 선 조치 이후 본 관리 기준을 수정 공시하겠습니다.
※기타 문의 사항은 데일리팜 운영자에게 연락주십시오. 메일 주소는 dailypharm@dailypharm.com입니다.









